QUICK SUMMARY:
SERP analysis involves evaluating Search Engine Result Pages (SERPs) to understand the content types (organic listings, ads, featured snippets) appearing for specific keywords. This process helps determine the search intent behind queries, analyze competition, and identify ranking patterns. This guide provides a comprehensive approach to SERP analysis, enhancing your agency’s understanding and ability to leverage SERPs to drive the maximum SEO value for clients.
“Can we get our website to Google’s first page by tomorrow?”
How often have you gotten this type of outrageous client request? Sure, your agency makes things look oh-so-easy, but when it comes to a first page ranking, it’s really not.
But the fact remains that your clients depend on your expertise and guidance. After all, those SERPs are not going to conquer themselves.
You don’t have to perform SERP analysis magic or resort to a quick fix, though. Instead, it’s about having the right approach, such as conducting keyword research and monitoring the competition.
Even if results don’t happen overnight, slow and steady wins the race. Achieving long-term SERP success is a great way to demonstrate expertise and keep clients coming back for more.
In this article, we’ll explore the importance of conducting SERP analysis, all the steps involved, and how it’s used to boost rankings.
Read on to learn more about:
-
What Is a SERP Analysis?
-
10 Types of SERP Features to Monitor
-
How To Conduct a Comprehensive SERP Analysis
-
5 Best Tools for SERP Analysis
What Is a SERP Analysis?
A Search Engine Results Page analysis means examining what’s displayed after inputting a target keyword into the Google search bar.
While it requires some groundwork, it’s a must-have strategy to improve your client’s SERP ranking. Here’s a breakdown of why it’s worth investing in.
| Understand Search Intent | A SERP analysis reveals deeper insights about user intent, such as commonly used keywords and related searches. |
| Scope the Competition | Analyzing a competitor’s SERP presence reveals their marketing strategies and uncovers opportunities for differentiation. |
| Execute Keyword Research | A SERP analysis helps discover user-relevant phrases, especially from SERP features like the People Also Ask (PAA) section. |
| Identify Top Local Businesses | See the top-rated websites for specific geographic areas. This provides a realistic look at the local business landscape. |
| Great for Content Ideas | Exploring the SERPs is a strategic way to get inspiration, expand existing strategies, and produce search-relevant content. |
| Determine Areas for Optimization | Use a SERP analysis to identify content gaps, missing metadata, slow-loading scripts, or other optimization issues. |
10 Types of SERP Features to Monitor
Before jumping into the analysis bit, it’s essential to understand the different SERP features. Here are the top ones to know.
1. Organic Listings
Organic listings are those search results that appear without any ad spend. These results are determined by Google’s algorithm, which ranks pages based on keyword relevance, authority, content quality, and user experience. If a website shows up favorably on the SERPs, it may mean the following:
- The content piece is considered valuable, informative, and engaging to users.
- The website has followed SEO best practices (e.g., using user-relevant keywords, rich metadata, and fast page load times).
- Content is regularly updated and fresh, which is favored by Google (and other search engines).
- Reputable sources link to this website, which indicates a strong backlink profile.
- The website offers a positive user experience, such as fast Page Load Times, a high Accessibility Score, and mobile responsiveness.
Although SEO efforts take time to produce ROI, high organic search rankings lead to increased traffic rates and even less reliance on advertising.
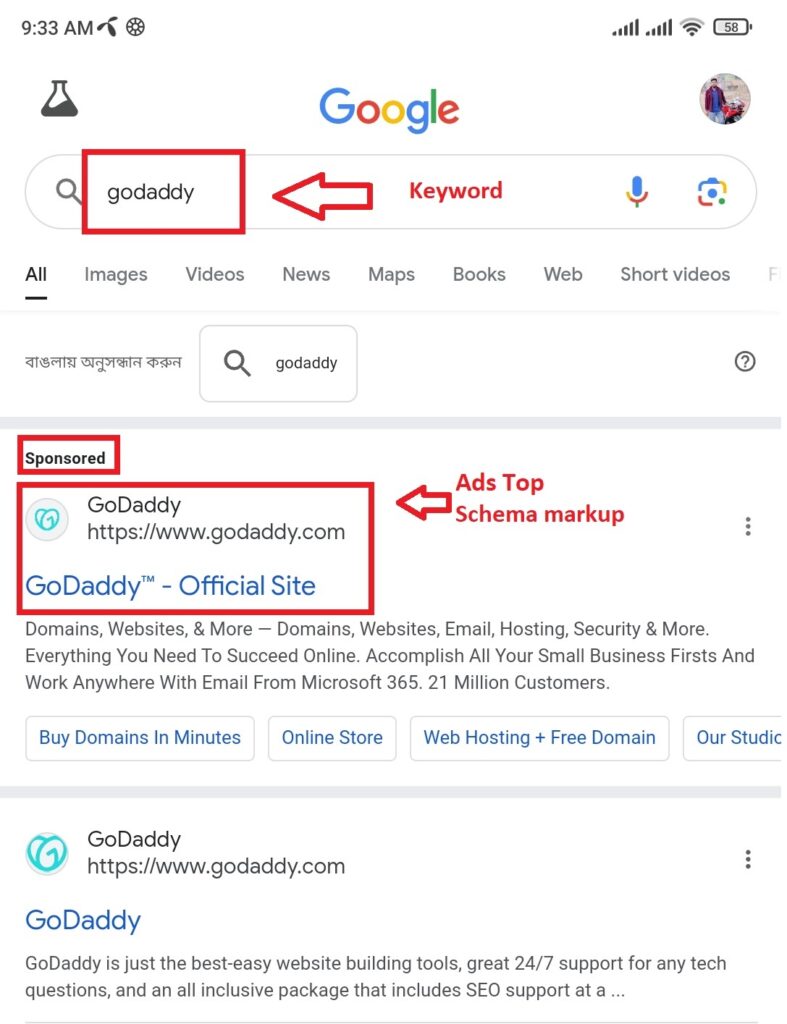
2. Paid Listings
If your clients need an extra boost, paid search listings are the way to go. They’re displayed at the top or side of organic listings, indicated by a “Sponsored” subtext. Here’s an example with both of these listings below.
A paid listing is useful for:
- Boosting website traffic quickly, which is handy for clients with limited brand visibility.
- Getting traction for time-sensitive events (e.g., form signups for an in-person event).
- Meeting other conversion-oriented goals (such as online sales).
While there are certainly benefits, paid search ads require strategic effort. This includes choosing an appropriate bidding strategy, setting a competitive budget, and creating a well-functioning landing page.
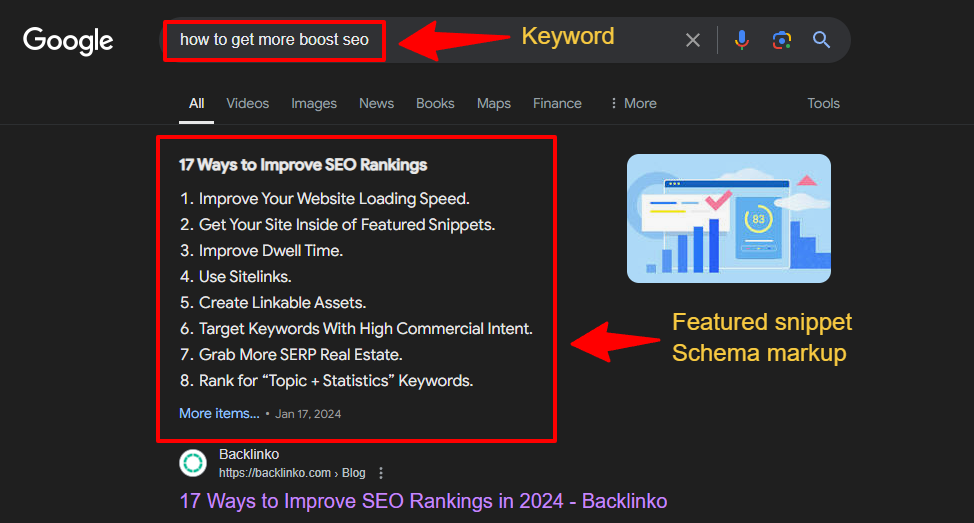
3. Featured Snippets
Ever seen this type of text on SERPs?
It’s a featured snippet–a concise and informative description that links to a website.
It appears above all other listings, meaning there’s high visibility and the possibility of increased Click-through Rates. This makes it one of the most desirable SERP features.
Here’s the thing–you can’t control whether your client’s website shows up in featured snippets. To increase the chances of this happening, create well-organized content that directly answers user questions.
Also known as “Position 0” on the SERPs, a Featured Snippet can get thousands upon thousands of eyes on your content! Featured Snippets are powerful, but you need to be very careful with how you go about getting them. Focus on high-quality content that is well structured, has proper schema attributed to it, and includes proper keywords to answer a user’s question.
Additionally, infuse search-relevant keywords in their content, headers, and Alt text. This makes it easier for Google to recognize and extract this information.
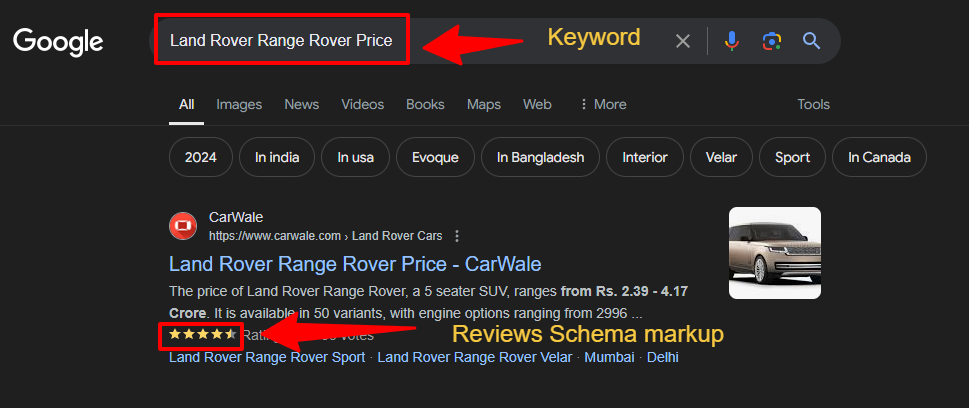
4. Rich Results
Rich results (also known as rich snippets) are additional details on a SERP beyond metadata. Essentially, they’re extra details to help users gather information quickly and choose the most relevant option. Rich results may include a variety of features, depending on the content. This may include:
- User ratings.
- Number of reviews.
- Type of business.
- Product price.
- Delivery times.
- Images or videos.
- Recipe-related details (e.g., time to prepare, number of calories per dish).
Optimize for rich results by including structured data on your client’s website (e.g., microdata, JSON-LD). After you’ve completed this step, use a tool like Google Rich Results Test to see what may be displayed on search results.
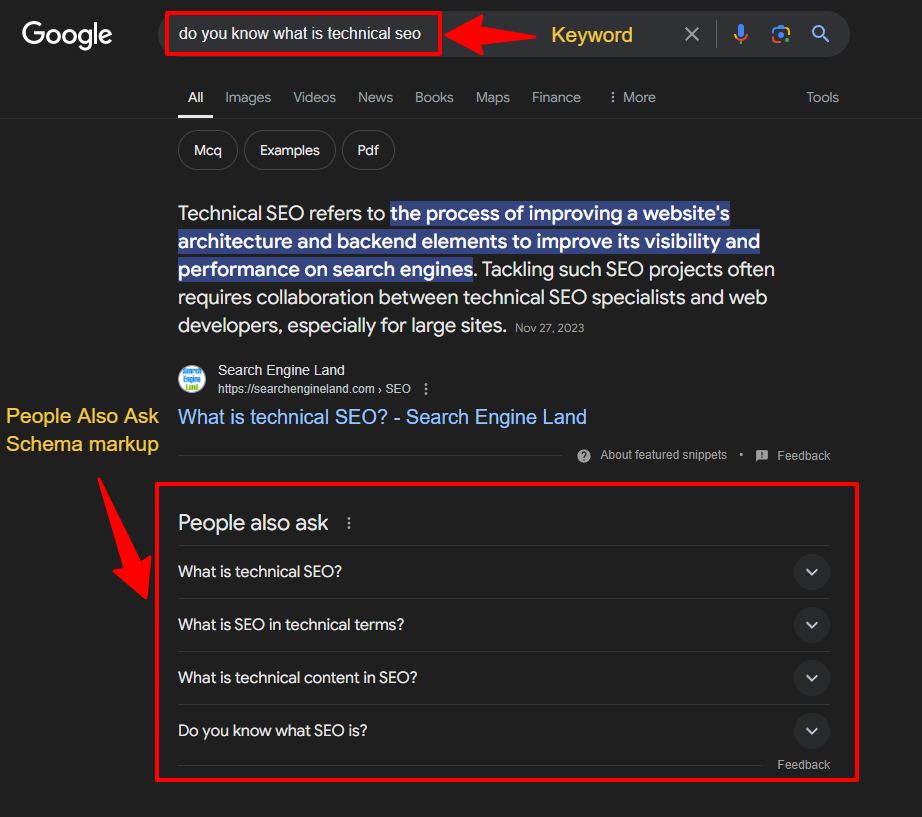
5. People Also Ask (PAA) Section
As the name suggests, the People Also Ask (PAA) section shows related questions from other users. Aside from answering anticipated questions, it’s an opportunity to explore long-tail keywords. Use this information to add keyword diversity and attract a highly targeted audience.
Clicking on any of these questions reveals a rich result with a description and website link.
Look at the “People Also Asked” questions and results to ensure your client has content depth. Users scan more than they read. However, Google needs enough meat in the content to make it relevant for the keywords and topic. Focus on the user first and the search engines second.
Similar to featured snippets, ensure your client’s content sufficiently addresses user concerns and is optimally formatted. This will increase the chances of showing up on the PAA section.
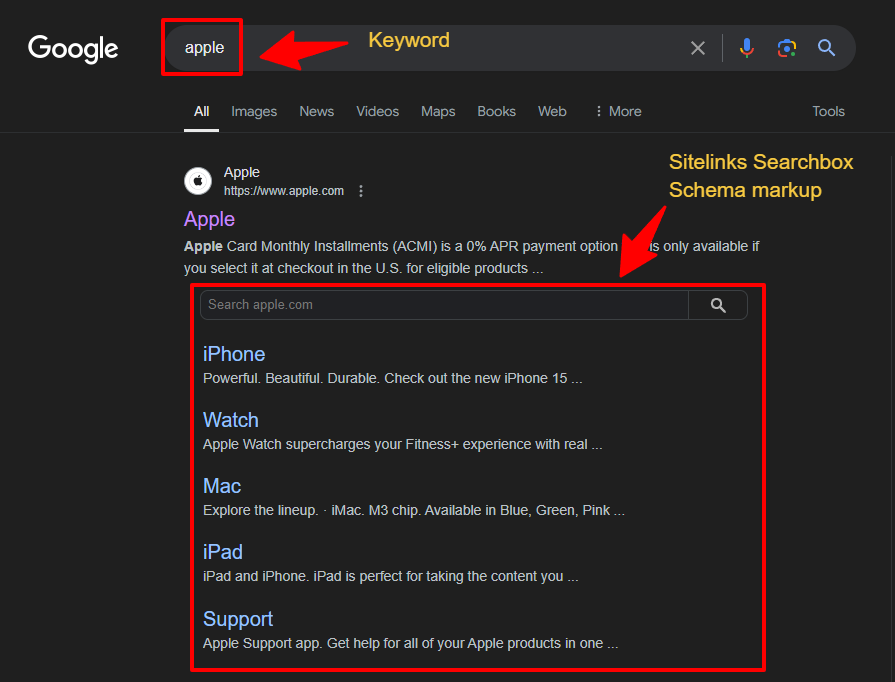
6. Sitelinks
Sitelinks are additional links to subpages of a website, displayed directly beneath the primary domain on a SERP. They offer users quick access to specific content, which saves time and effort.
Google’s algorithm automatically generates sitelinks, typically based on a user’s search query and its relevance to subpages. Since sitelinks improve SEO analytics like Impressions and Click-through Rates (CTRs), ensure your client’s website is well-structured.